Air-gapped Installation Guide for OpenShift Environments#
This guide explains how to install the AMD GPU Operator in an air-gapped environment where the OpenShift cluster has no external network connectivity.
Prerequisites#
OpenShift 4.16+
Users should have followed the OpenShift Official Documentation to install the air-gapped cluster and set up a Mirror Registry.
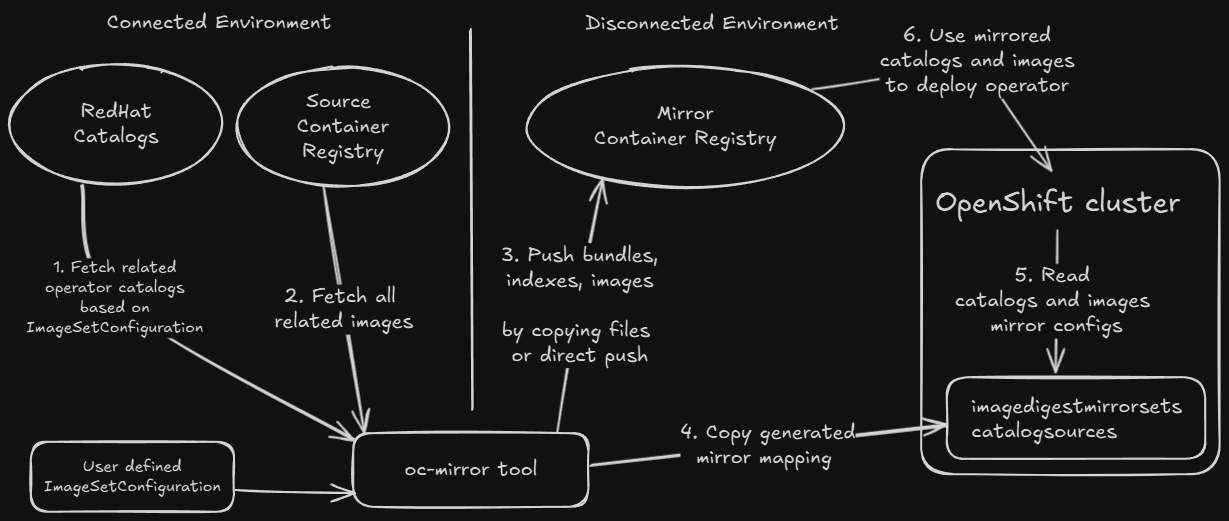
Note
Users only need to provide the
ImageSetConfigurationto configure operator catalogs and images for mirroring artifacts into the mirror container registry.Users may need to manually copy mirrored artifacts to the air-gapped system if the jump host cannot directly push images to the mirror container registry.
Most steps in the diagram above are automatically completed by
oc-mirrorand other Red Hat provided tools, which can be downloaded from the OpenShift official website.
Here is an example ImageSetConfiguration for mirroring the required catalogs and images for the AMD GPU Operator into your mirror registry.
Warning
The following
ImageSetConfigurationfile is an incomplete example.Users must configure the
storageConfigsection for either directly pushing artifacts to the mirror container registry or saving to local file storage.Users may merge the
mirrorsection of this example with their ownImageSetConfiguration.Detailed explanation of
ImageSetConfigurationcan be found in the OpenShift official documentation.When mirroring the source image
docker.io/rocm/amdgpu-driver, we strongly recommend making it accessible without requiring image pull secrets. If image pull secrets are required for pulling the source image, refer to the notes in Driver Installation to configure the pull secret.
# oc-mirror --v2 compatible ImageSetConfiguration
kind: ImageSetConfiguration
apiVersion: mirror.openshift.io/v1alpha2
mirror:
# in this file we use 4.19 as an example
# please adjust the OpenShift version if needed
platform:
graph: true
channels:
# adjust the minor version and patch version if needed
- name: stable-4.19
minVersion: 4.19.13
maxVersion: 4.19.13
operators:
- catalog: registry.redhat.io/redhat/redhat-operator-index:v4.19 # adjust the OpenShift version if needed
packages:
# Node Feature Discovery (NFD)
- name: nfd
minVersion: "4.19.0-202509300824" # adjust the version if needed
channels:
- name: stable
# Kernel Module Management (KMM)
- name: kernel-module-management
minVersion: "2.4.1" # adjust the version if needed
channels:
- name: stable
- name: release-2.4
# AMD GPU Operator (Certified)
# To get full list of released version
# Either go to OperatorHub
# Or check https://github.com/redhat-openshift-ecosystem/certified-operators/tree/main/operators/amd-gpu-operator
- catalog: registry.redhat.io/redhat/certified-operator-index:v4.19 # adjust the OpenShift version if needed
packages:
- name: amd-gpu-operator
minVersion: "1.4.1" # adjust the version if needed
channels:
- name: alpha
# adjust the image tags if needed
additionalImages:
- name: registry.redhat.io/ubi9/ubi:latest
- name: registry.redhat.io/ubi9/ubi-minimal:latest
- name: docker.io/rocm/gpu-operator:v1.4.1
- name: docker.io/rocm/gpu-operator-utils:v1.4.1
- name: docker.io/busybox:1.36
- name: docker.io/rocm/device-metrics-exporter:v1.4.1
- name: docker.io/rocm/test-runner:v1.4.1
- name: docker.io/rocm/device-config-manager:v1.4.1
- name: docker.io/rocm/rocm-terminal:latest
- name: docker.io/rocm/k8s-device-plugin:latest
- name: docker.io/rocm/k8s-node-labeller:latest
# adjust RHEL version and ROCm version if needed for source image
# image tag format for CoreOS is coreos-<RHEL version>-<ROCm version>
- name: docker.io/rocm/amdgpu-driver:coreos-9.6-7.0.2
helm: {}
After mirroring setup, users should have installed NFD and KMM, and enabled the internal image registry in the air-gapped cluster. See OpenShift OLM Installation for details.
Users should have installed the AMD GPU Operator in the air-gapped cluster without creating a
DeviceConfig.
Installation Steps#
Note
Starting from AMD GPU Operator v1.4.1, building the amdgpu driver directly within the disconnected cluster is supported.
Option 1: Follow steps 1 and 2 to prepare a pre-compiled driver image in a connected environment, then import the pre-compiled image into the disconnected cluster.
Option 2: Skip preparing a pre-compiled driver image and go directly to step 3, ensuring that:
The source image
docker.io/rocm/amdgpu-driveris properly mirrored into your mirror image registry in the disconnected environment.The
oc-mirrorgeneratedImageDigestMirrorSetandImageTagMirrorSetare applied.
1. Build Precompiled Driver Image#
Build the pre-compiled driver image in a build cluster that has internet access by following Preparing Pre-compiled Driver Images and the steps for OpenShift.
After successfully pushing the driver image, save it by running:
If you are using OpenShift internal registry
podman login -u deployer -p $(oc create token deployer) image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000
podman pull image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/default/amdgpu_kmod:coreos-9.6-5.14.0-570.45.1.el9_6.x86_64-7.0
podman save image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/default/amdgpu_kmod:coreos-9.6-5.14.0-570.45.1.el9_6.x86_64-7.0 -o driver-image.tar
If you are using other image registry
podman login -u username -p password/token registry.example.com
podman pull registry.example.com/amdgpu_kmod:coreos-9.6-5.14.0-570.45.1.el9_6.x86_64-7.0
podman save registry.example.com/amdgpu_kmod:coreos-9.6-5.14.0-570.45.1.el9_6.x86_64-7.0 -o driver-image.tar
2. Import Pre-compiled Driver Image#
A. Import images
Note
This step is for using the pre-compiled driver image within the OpenShift internal registry (the OpenShift built-in image registry, not the mirror registry for air-gapped installation).
Users who have already pushed the pre-compiled driver image to another registry don’t need to manually load it into the internal registry. Skip to step 3 and specify the image URL in
spec.driver.image.
Import pre-compiled driver image
After copying the image files to the air-gapped cluster, switch to the air-gapped cluster and use podman to load the image, re-tag if needed, then push the image to the desired image registry:
Load the image file:
podman load -i driver-image.tarRe-tag if needed:
podman tag <old tag> <new tag>. Remember to tag the image to the GPU operator’s namespace. For example, if using the GPU operator inopenshift-amd-gpu, tag the image toimage-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/openshift-amd-gpu/amdgpu_kmod.Use podman to log in to the image registry if needed. For OpenShift internal registry:
podman login -u builder -p $(oc create token builder) image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000
Push the image:
podman push <new tag>
B. Verify that the required images are located in the internal registry.
For example, if using the internal registry:
$ oc get is -n openshift-amd-gpu
NAME IMAGE REPOSITORY TAGS UPDATED
amdgpu_kmod image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/openshift-amd-gpu/amdgpu_kmod coreos-9.6-5.14.0-570.19.1.el9_6.x86_64-6.4.1 3 days ago
3. Deployment of DeviceConfig in Air-gapped Environment#
A. If pre-compiled driver images are present, the operator will directly pull and use the pre-compiled driver image.
B. If pre-compiled driver images are not present, the operator will build the kernel module based on the mirrored source image, which was previously mirrored from docker.io/rocm/amdgpu-driver.
apiVersion: amd.com/v1alpha1
kind: DeviceConfig
metadata:
name: test-deviceconfig
namespace: openshift-amd-gpu
spec:
driver:
# Specify image repo here if NOT using OpenShift internal registry without image tag
# Default value for OpenShift is image-registry.openshift-image-registry.svc:5000/$MOD_NAMESPACE/amdgpu_kmod
#image: registry.example.com/amdgpu_kmod
enable: true
# For OpenShift, set useSourceImage to true
# to enable building driver from source code image in air-gapped environment
useSourceImage: true
version: "7.0"
devicePlugin:
enableNodeLabeller: true
metricsExporter:
enable: true
selector:
feature.node.kubernetes.io/amd-gpu: "true"
4. Verify the Deployment of DeviceConfig#
After successfully building the driver image and loading the amdgpu kernel modules, the metrics exporter and device plugin pods should be running in the same namespace as the DeviceConfig.
$ oc get pods -n openshift-amd-gpu
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
amd-gpu-operator-controller-manager-d7654f88d-4x4tx 1/1 Running 0 6h45m
test-cr-device-plugin-5w7dp 1/1 Running 0 2m
test-cr-metrics-exporter-5xwwr 1/1 Running 0 2m
If the driver loaded correctly without any issues, the device plugin will start advertising resources. If the device plugin is running but the node still shows zero amd.com/gpu, check the device plugin pod logs or dmesg on the node to detect potential failures.
$ oc get node -oyaml | grep amd.com
gpu.operator.amd.com/openshift-amd-gpu.test-cr.driver: container
amd.com/gpu: "1"
amd.com/gpu: "1"