Introduction#
This reference design establishes a comprehensive, automated health check framework for AMD Instinct™ GPU infrastructure using the AMD GPU Operator’s AGFHC (AMD GPU Fleet Health Check) capability. It covers the complete GPU node lifecycle—from initial deployment through production operations, maintenance, and expansion—and gates every new Instinct GPU node with a 24-hour burn-in plus real-time acceptance checks.
Acceptance criteria enforced during burn-in#
100% tests pass continuously for 24h
No thermal throttling
Power within spec (instantaneous cap with tolerance)
UE = 0 (no uncorrectable ECC)
This Design Automates#
24 hour GPU stress test
Continuous telemetry and fault detection
Automated verdict + node promotion
Operator-managed GPU plugin and metrics exporter
Core Components#
Kubernetes — schedules validation workloads and remediation jobs
AMD GPU Operator + AGFHC — driver lifecycle, device plugin, ongoing fleet health checks
Burn-In Pipeline — 24h stress for Instinct GPU nodes with AMD Test Runner (RVS) + telemetry gate
Observability —
amd-smitelemetry (power/thermals/RAS) + artifacts for auditControl Primitives — node labels/taints for isolation; Jobs for tests; optional auto-promotion controller
High-Level Design#
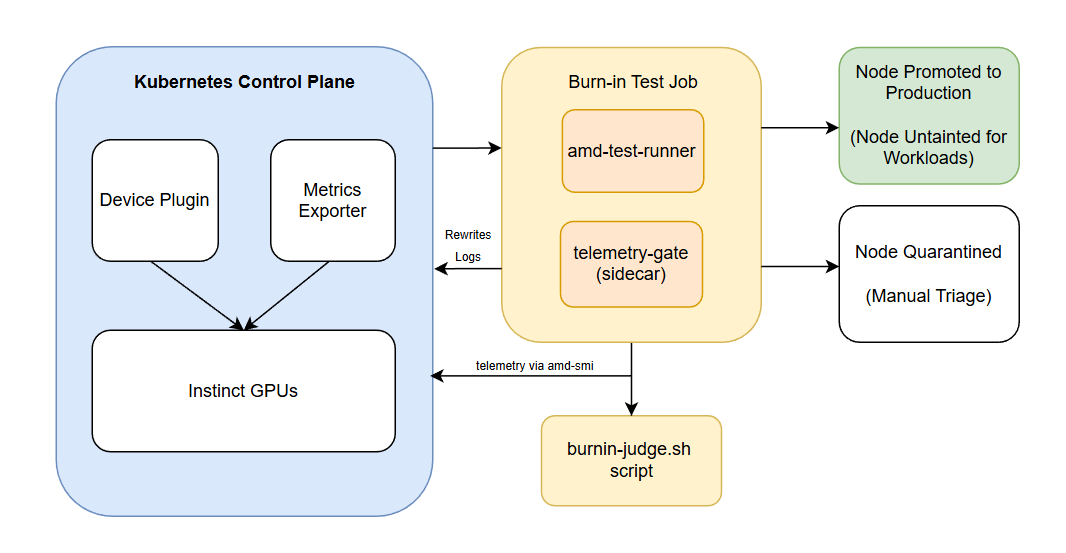
Flow Summary#
Operator and Pre-requisites
Install GPU Operator and confirm device plugin running and apply the relevant ConfigMaps
Burn-in Test
A test runner job executes for 24 hours and telemetry gate samples every 10 seconds checking for any throttle/power/UE violations
Burnin Judge container waits for job completion and copies /gate/summary.txt
PASS:
Node gets:
gpu.amd.com/burnin=doneNode stays tainted → remains isolated until you explicitly promote it
Very safe for production clusters
No risk of premature production scheduling
FAIL:
Node gets:
gpu.amd.com/burnin=failedNode remains tainted (stage=burnin) → stays isolated for triage
No extra fail-taint manipulation
Promotion
Optionally change gpu.amd.com/stage from burnin → prod for production schedulers
Prerequisites#
System Requirements#
Kubernetes cluster v1.29.0 or later
Helm v3.2.0 or later
kubectlcommand-line tool configured with access to the clusterCluster admin privileges
Cluster Requirements#
A functioning Kubernetes cluster with:
All system pods running and ready
Properly configured Container Network Interface (CNI)
Required Access#
Access to pull images from:
AMD’s container registry or your configured registry
Public container registries (Docker Hub, Quay.io)
Pre-Installation Steps#
1. Verify Cluster Status#
Check that your cluster is healthy and running:
kubectl get nodes
kubectl get pods -A
Expected output should show:
All nodes in
ReadystateSystem pods running (kube-system namespace)
CNI pods running (e.g., Flannel, Calico)
Example of a healthy cluster:
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-7krtk 1/1 Running 0 10d
kube-system coredns-7db6d8ff4d-644fp 1/1 Running 0 2d20h
kube-system kube-apiserver-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 64d
kube-system kube-controller-manager-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 64d
kube-system kube-scheduler-control-plane 1/1 Running 0 64d
2. Verify GPU Operator Setup#
Check to ensure all components of the GPU Operator are running:
kubectl get pods -n kube-amd-gpu
Expected Output:
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gpu-operator amd-gpu-operator-controller-manager-6954b68958-ljthg 1/1 Running 0 2m
gpu-operator amd-gpu-kmm-controller-59b85d48c4-f2hn4 1/1 Running 0 2m
gpu-operator amd-gpu-kmm-webhook-server-685b9db458-t5qp6 1/1 Running 0 2m
gpu-operator amd-gpu-nfd-gc-98776b45f-j2hvn 1/1 Running 0 2m
gpu-operator amd-gpu-nfd-master-9948b7b76-ncvnz 1/1 Running 0 2m
gpu-operator amd-gpu-nfd-worker-dhl7q 1/1 Running 0 2m
If GPU Operator is not setup, please refer to GPU Operator for installation
Deployment Runbook#
1. Prepare Namespace#
kubectl create namespace kube-amd-gpu --dry-run=client -o yaml | kubectl apply -f -
2. Isolate the Node#
NEW_NODE=<node-name>
kubectl label node $NEW_NODE gpu.amd.com/stage=burnin --overwrite
kubectl taint nodes $NEW_NODE gpu.amd.com/burnin=running:NoSchedule
3. Deploy Burn-in#
Deployment Manifests#
Download GPU Service Account YAML
Download Burnin Telemetry ConfigMap YAML
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu apply -f sa-gpu-burnin.yaml
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu apply -f cm_rvs_burnin.yaml
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu apply -f cm_burnin_telemetry.yaml
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu apply -f job_24h.yaml
4. Monitor#
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu logs -f job/mi300-burnin-24h -c amd-test-runner
kubectl -n kube-amd-gpu logs -f job/mi300-burnin-24h -c telemetry-gate
5. Validation Checks#
kubectl get nodes --show-labels | grep burnin
kubectl describe node <node> | grep Taints
6. Post-Checks#
Check |
Command |
Expected |
|---|---|---|
GPU allocatable |
|
8 |
Telemetry Summary |
|
No violations |