Quick Start Guide#
This section provides a step-by-step guide to install the AMD Container Toolkit and configure your system for Docker-based GPU container workloads. The steps below are tailored for ease of use, production-readiness, and ensuring compatibility across AMD Instinct GPU-enabled systems.
Prerequisites#
Before installing the AMD Container Toolkit, ensure the following dependencies are installed.
- Docker:
The toolkit is designed to work with Docker, so ensure you have Docker installed on your system.
Docker version 25.0 or newer is required for all features.
Note
The Container Device Interface (CDI) format, used by modern container runtimes to abstract and expose GPUs, is not supported in older Docker versions.
Without Docker 25+, CDI functionality such as dynamic device enumeration and CDI-style run commands will not work as intended.
Docker version 28.3.0 or newer is required to use the standardized
--gpusflag for AMD GPU selection.
sudo apt-get install docker.io
You can verify your Docker version using:
docker --version
If you are on an earlier Docker version, please upgrade to at least Docker 25 before proceeding with toolkit configuration and GPU-based workloads.
ROCm:
ROCm 6.4.1 or newer is required to view and verify partitioned GPUs inside containers.
jq - Required during uninstallation to parse configuration settings cleanly.
sudo apt-get install jq
Step 1: Update System and Group Settings#
Update your system:
sudo apt update
Add your user to the required groups for GPU device access:
sudo usermod -a -G render,video $LOGNAME
Step 2: Install the AMDGPU Driver#
Refer to the latest ROCm documentation for driver installation here, ROCm Install Quick Start.
Download the AMDGPU driver installer package from the Radeon Repository.
Install the downloaded package.
Load the driver.
#Example (for Ubuntu 22.04, ROCm 6.3.4)
wget https://repo.radeon.com/amdgpu-install/6.3.4/ubuntu/jammy/amdgpu-install_6.3.60304-1_all.deb
sudo apt install ./amdgpu-install_6.3.60304-1_all.deb
sudo apt update
amdgpu-install --usecase=dkms
sudo modprobe amdgpu
Step 3: Configure Repositories#
Install required dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install vim wget gpg
Create keyrings directory:
sudo mkdir --parents --mode=0755 /etc/apt/keyrings
Install GPG keys and repository links:
wget https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/rocm.gpg.key -O - | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/keyrings/rocm.gpg > /dev/null
Add the AMD Container Toolkit repository.
Ubuntu 22.04:
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/rocm.gpg] https://repo.radeon.com/amd-container-toolkit/apt/ jammy main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/amd-container-toolkit.list
Ubuntu 24.04:
echo "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/rocm.gpg] https://repo.radeon.com/amd-container-toolkit/apt/ noble main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/amd-container-toolkit.list
Update package index and install the toolkit:
sudo apt update
RHEL 9.5:
tee --append /etc/yum.repos.d/amd-container-toolkit.repo <<EOF
[amd-container-toolkit]
name=amd-container-toolkit
baseurl=https://repo.radeon.com/amd-container-toolkit/el9/main/
enabled=1
priority=50
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://repo.radeon.com/rocm/rocm.gpg.key
EOF
Step 4: Install Toolkit and Docker#
Ubuntu:
sudo apt install amd-container-toolkit
RHEL 9.5:
Clean the package cache and install the toolkit:
dnf clean all
dnf install -y amd-container-toolkit
Step 5: Configure Docker Runtime for AMD GPUs#
Register the AMD container runtime and restart the Docker daemon:
sudo amd-ctk runtime configure
sudo systemctl restart docker
This configuration ensures that Docker is aware of the AMD container runtime and is able to support GPU-accelerated workloads using AMD Instinct devices.
Step 6: Verify Container Runtime Installation#
To run Docker containers with access to AMD GPUs, you need to specify the AMD runtime and visible GPUs. Here are some examples you can use to verify the installation:
Run a container with access to all available AMD GPUs:
docker run --runtime=amd -e AMD_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 amd-smi monitor
Output should look like this, validating that all GPUs are visible:
GPU POWER GPU_T MEM_T GFX_CLK GFX% MEM% ENC% DEC% VRAM_USAGE
0 137 W 41 °C 36 °C 142 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
1 139 W 39 °C 33 °C 135 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
2 138 W 42 °C 34 °C 145 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
3 141 W 39 °C 33 °C 139 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
4 140 W 42 °C 36 °C 146 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
5 137 W 38 °C 33 °C 133 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
6 139 W 43 °C 36 °C 151 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
7 137 W 41 °C 34 °C 141 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
Run a container with access to a specific AMD GPU (i.e., the first GPU):
docker run --runtime=amd -e AMD_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 amd-smi monitor
Output should look like this, validating that only the first GPU is visible:
GPU POWER GPU_T MEM_T GFX_CLK GFX% MEM% ENC% DEC% VRAM_USAGE
0 140 W 42 °C 36 °C 146 MHz 0 % 0 % N/A 0 % 0.3/192.0 GB
Using --gpus Flag with Docker 28.x+#
Starting from Docker 28.3.0, containerized GPU workloads can leverage the standardized --gpus flag for specifying AMD GPU usage. The AMD Container Toolkit integrates seamlessly with this interface, enabling users to declare GPU requirements directly in docker run commands.
Examples
Use all available GPUs
sudo docker run --rm --runtime=amd --gpus all rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 rocm-smi
or equivalently:
sudo docker run --rm --runtime=amd --gpus device=all rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 rocm-smi
Use any 2 GPUs
sudo docker run --rm --runtime=amd --gpus 2 rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 rocm-smi
Note
Specifying multiple values in a comma-separated list like
--gpus 1,2,3will result in only the last number being recognized. For instance, that same input would end up requesting 3 GPUs.Select a specific set of GPUs
sudo docker run --rm --runtime=amd --gpus '"device=1,2,3"' rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 rocm-smi
Note
GPU indices start from 0.
The
device=specifier is mandatory when enumerating specific GPUs.
Select one specific GPU
sudo docker run --rm --runtime=amd --gpus device=2 rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 rocm-smi
Note
Again, the ``device=`` prefix is required.
Summary
Use
--gpus <count>to request a specific number of GPUs (e.g.,--gpus 2)Use
--gpus device=<i,j,...>to request exact GPU indices (e.g.,device=1,2,3)
GPU Partitioning: Enabling Fine-Grained Resource Allocation#
GPU partitioning empowers users to divide a single physical GPU into multiple logical units, each of which can be independently accessed and managed within containerized workloads. This capability is essential for fine-grained control over GPU resources, enabling scenarios such as workload isolation, resource sharing, and maximizing GPU utilization within containerized environments.
Starting with version 1.1.0, the AMD Container Toolkit introduces full support for GPU partitioning
Note
Partitioned GPUs behave identically to physical GPUs within containers. Applications and monitoring tools like rocm-smi or amd-smi will detect and report them as separate devices.
Partitioning Schemes and Access#
With the AMD Container Toolkit, you can apply various partitioning schemes to your GPUs. Once partitioned, each logical GPU appears to the container runtime as a distinct device, indistinguishable from a standard, unpartitioned GPU. This allows you to allocate specific GPU partitions to different containers, optimizing performance and isolation. This functionality is particularly useful in multi-tenant or resource-constrained environments where full GPU allocation is not necessary.
Regenerating and Validating CDI Specifications#
Whenever you modify the GPU partitioning on your system, it is must to regenerate the Container Device Interface (CDI) specification. This ensures that the container runtime is aware of the current GPU topology and can accurately expose the correct devices to your containers.
You can regenerate and validate the CDI spec either by specifying an explicit output path or by using the default location.
To regenerate the CDI spec with an explicit output path after a partitioning change, run:
amd-ctk cdi generate --output=/etc/cdi/amd.json
To validate that the existing CDI spec accurately reflects the available GPUs and partitions, use:
amd-ctk cdi validate --path=/etc/cdi/amd.json
Alternatively, you may omit the path to use the default CDI spec location:
amd-ctk cdi generate
amd-ctk cdi validate
Note
If you do not specify an output or path, the commands will operate on the default CDI spec location as defined by the toolkit. This is suitable for most standard installations.
Inspecting GPU Partition Status#
You can use the amd-smi tool inside your container to inspect the status of each GPU, determine whether it is partitioned or unpartitioned, and view details about the partitioning scheme in use.
docker run --rm --runtime=amd -e AMD_VISIBLE_DEVICES=all rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 amd-smi
Selecting GPUs and Partitions#
Partitioning can result in a large number of logical GPUs on your system. To simplify device selection, the AMD Container Toolkit supports specifying a range or set of GPUs using the AMD_VISIBLE_DEVICES environment variable. For example:
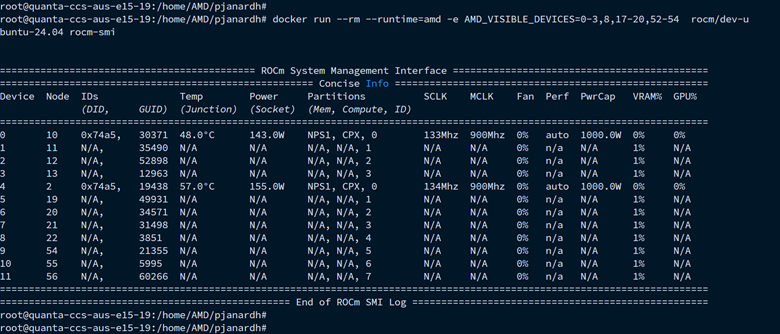
docker run --rm --runtime=amd -e AMD_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0-3,8,17-20,52-54 rocm/dev-ubuntu-24.04 amd-smi
This command grants the container access to GPUs 0 through 3, 8, 17 through 20, and 52 through 54. The range specifier is especially useful for efficiently targeting all partitions within specific physical GPUs, as partitions are typically numbered contiguously.
Note
To view and verify partitioned GPUs inside containers, ensure you are using ROCm version 6.4.1 or newer.
Best Practices and Documentation#
Always regenerate the CDI spec after any GPU partitioning change to ensure containers have access to the correct devices.
Validate the CDI spec to confirm it matches the current system state before launching new workloads.
Consult the latest documentation for detailed partitioning workflows and troubleshooting guidance.
By leveraging GPU partitioning, you can achieve fine-grained resource allocation, improved workload isolation, and greater flexibility in deploying GPU-accelerated containers across your infrastructure.
Uninstallation Guide#
To remove the amd-container-toolkit, you must have jq installed. The uninstallation script relies on it to parse configuration files.
sudo apt-get install jq
Then proceed with the removal:
sudo apt-get remove --purge amd-container-toolkit
If you encounter issues, inspect the logs:
sudo journalctl -u apt
sudo tail -f /var/log/amd-container-runtime.log
If you continue to face errors, you may need to force the removal:
sudo dpkg --remove --force-all amd-container-toolkit
sudo apt-get autoremove